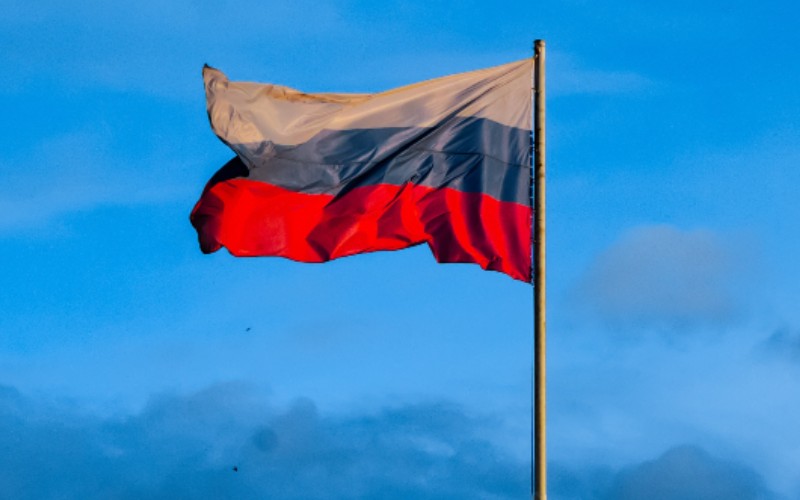
Cryptoassets have been included in an unprecedented package of economic sanctions imposed on Russia and Belarus.
The UK and other countries have imposed the sanctions in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine on 24th February.
The UK financial regulatory authorities reiterated that all UK financial services firms, including the cryptoasset sector, are expected to play their part in ensuring that sanctions are complied with.
A joint statement from UK financial regulatory authorities said they were working closely with partners in government and law enforcement here and abroad to share intelligence and act to prevent sanctions evasion.
“Financial sanctions regulations do not differentiate between cryptoassets and other forms of assets,” read the statement. “The use of cryptoassets to circumvent economic sanctions is a criminal offence under the Money Laundering Regulations 2017 and regulations made under the Sanctions and Anti-Money Laundering Act 2018.
“The FCA has already written to all registered cryptoasset firms and those holding temporary registration status to highlight the application of sanctions on various entities and individuals.
“We remind all other authorised financial institutions to check the FCA register to identify whether any cryptoasset firms they do business with are registered, or to check the equivalent register of the jurisdiction in which the cryptoasset firm is based.
“Both the FCA and the PRA will act if they see authorised financial institutions supporting cryptoasset firms operating in the UK illegally.”
They said controls developed to identify customers and monitor their transactions under the Money Laundering Regulations 2017 can help with compliance, but firms will need to implement additional sanctions specific controls as appropriate.
Where blockchain analytics solutions are deployed, this includes ensuring that compliance teams understand how these capabilities can be best used to identify transactions linked to higher-risk wallet addresses.
Red flag indicators of an increased risk of sanctions evasion may include the use of tools designed to obfuscate the location of the customer – for example, an IP address associated with a virtual private network or proxy, or the source of cryptoassets (e.g. mixers and tumblers).